How does a thermocouple (TC sensor) work?

How does a thermocouple (TC sensor) work?
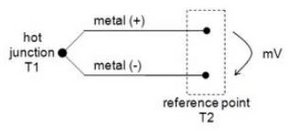
EPIC® SENSORS thermocouple sensor produces a mV measuring signal, which is proportional to temperature depending on which TC type is used.
Measuring principle
When two wires of different metals or metal alloys (thermo wires) are joined together in one end (hot junction), a thermocouple is formed. The free ends of those wires form a reference point. If there is a temperature difference between hot junction T1 and reference point T2, a thermal electromotive force (mV voltage) is created in the thermocouple, the level of this voltage is proportional only to temperature difference T1-T2 and to materials, which the thermocouple is formed of (Seebeck effect).
For that reason it is important to have the reference point as stable as possible, when it is moved to a location of standard temperature (reference temperature) using extension wire or insulated thermo wire. More details on page Compensating cables.
Cold Junction Compensating (CJC)
Temperature transmitter or measuring systems need information of the reference point (cold junction) temperature T2. Variations of reference point temperature are compensated with CJC measuring (Cold Junction Compensation). Temperature transmitters CJC measuring can be an internal function or a measuring resistance integrated in connectors. If the reference point is far away from the transmitter, a separate temperature measuring of that point has to be implemented and wired to transmitter as compensation signal.
Temperature ranges and tolerances of thermocouple types:
| Type | Accuracy class | Temperature range °C | Constant value °C | Tolerances allowed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | 1 2 3 | -40...+350 -40...+350 -200...+40 | ± 0,5 ± 1,0 ± 1,0 | ± 0,004 [t] ± 0,0075 [t] ± 0,015 [t] |
| E | 1 2 3 | -40...+800 -40...+900 -200...+40 | ± 1,5 ± 2,5 ± 2,5 | ± 0,004 [t] ± 0,0075 [t] ± 0,015 [t] |
| J | 1 2 | -40...+750 -40...+750 | ± 1,5 ± 2,5 | ± 0,004 [t] ± 0,0075 [t] |
| K | 1 2 3 | -40...+1000 -40...+1200 -200...+40 | ± 1,5 ± 2,5 ± 2,5 | ± 0,004 [t] ± 0,0075 [t] ± 0,015 [t] |
| N | 1 2 3 | -40...+1000 -40...+1200 -200...+40 | ± 1,5 ± 2,5 ± 2,5 | ± 0,004 [t] ± 0,0075 [t] ± 0,015 [t] |
| R ja S | 1 2 | 0...+1600 0...+1600 | ± 1,0 ± 1,5 | ± [1+(t-1100)×0,003] °C ± 0,0025 [t] |
| L* | -200...+400 +400...+900 | ± 3,0 °C ± 0,75 % |
* Type L is defined in standard DIN 43710, all other types in standard IEC 60584.
Materials and cables of thermocouple types
- Cable materials* are same or have same kind of electrical features as the thermocouple materials. More details on page: Compensating cables.
- Cable/wire colors** are according to standard IEC 60584, except for types U and L which are according to DIN 43710.






